Types of question blocks
Overview
In Qatalyst, there are a variety of question Blocks which you can add to your studies and conduct user research. You can also create questionnaires around your user research using the survey blocks available. Gather responses and later see the results in the form of charts in your study and analyse the respondent's responses. In this article, we will explore the different question types available on Qatalyst and how you can use them to gather valuable insights.
The question blocks are divided into the following categories:
- Survey Blocks
- Unmoderated Blocks
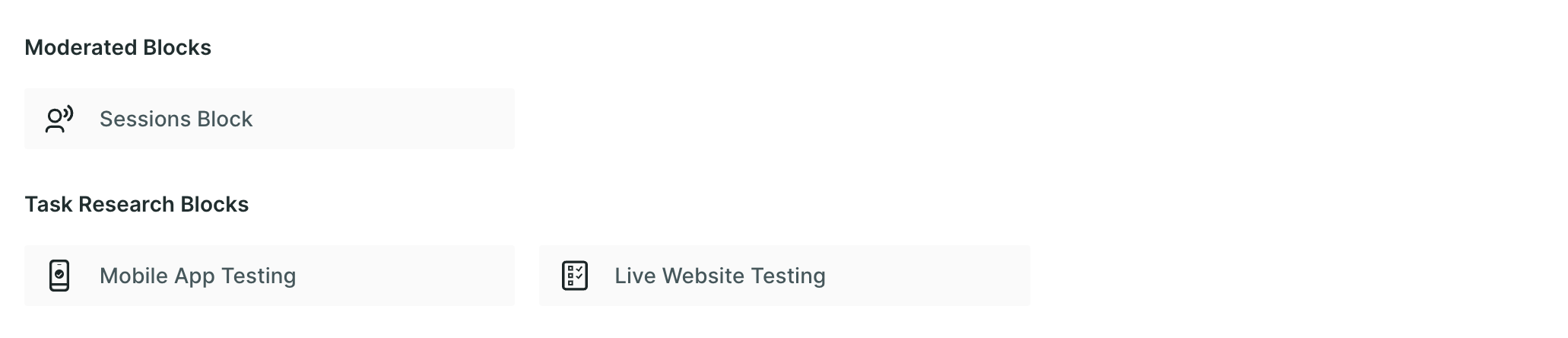
- Moderated Blocks
- Task Research Blocks
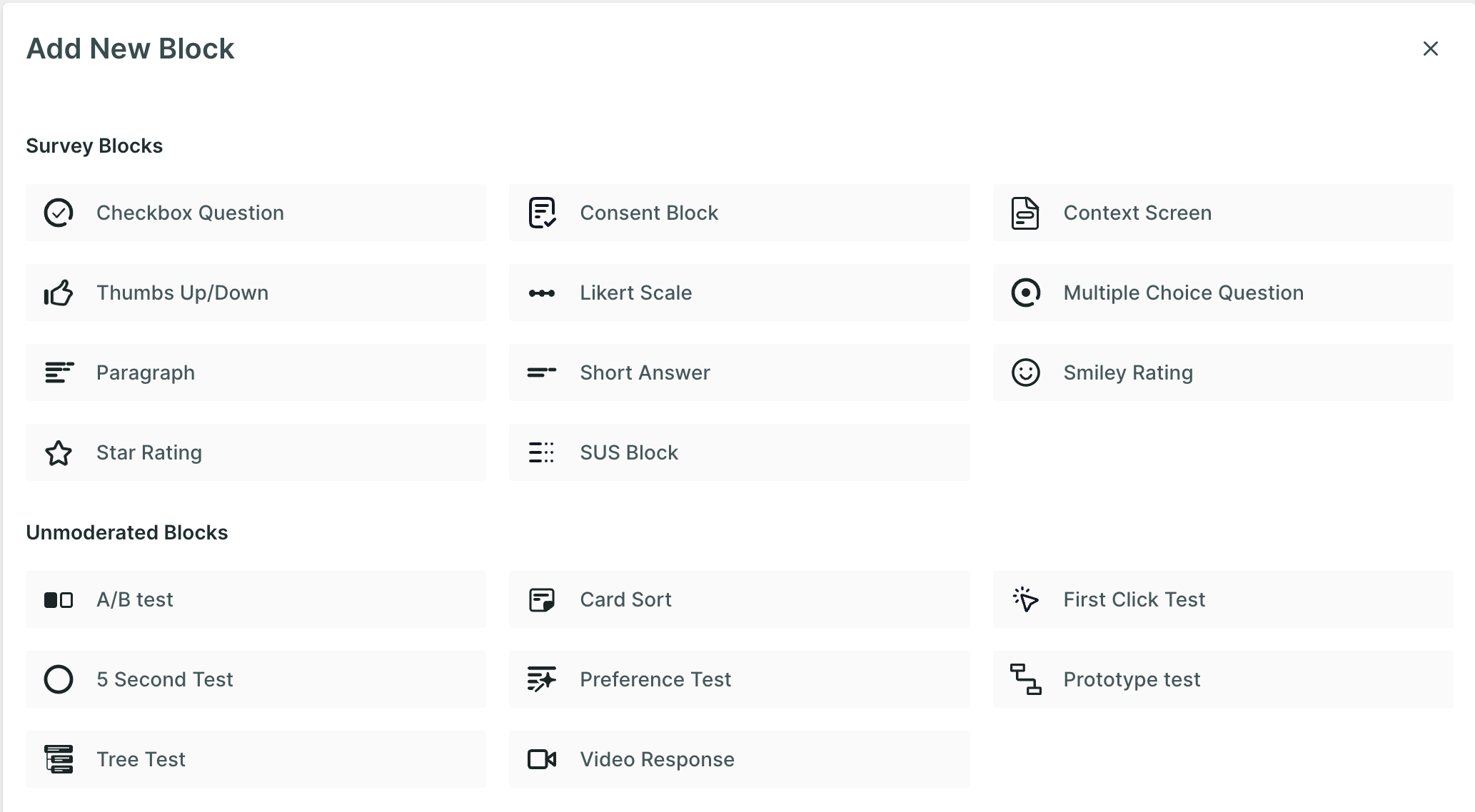
Survey Blocks
In the Survey section, you will find the different question types you can add to your study and gather quantitative data.
1. Checkbox Question: In this question type, the respondent can select multiple responses from the given list of options. In User Research, checkbox questions can be used to gather feedback on feature preferences, content preferences, or user behaviour patterns.
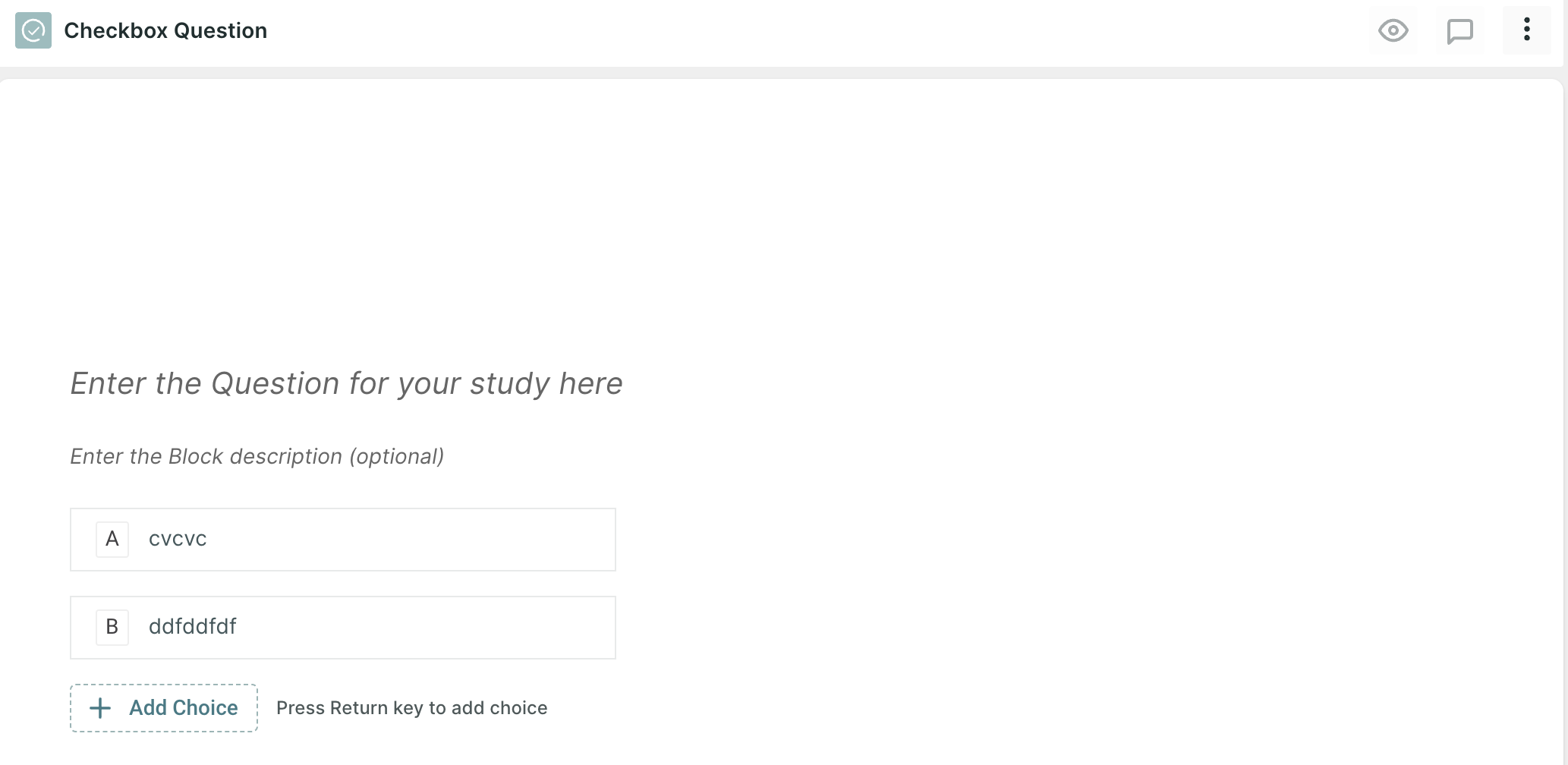
Question Example:
- Which elements caught your attention within the first 5 seconds?
- What adjectives would you use to describe your initial impression of the website?
- Which of the following features do you find most valuable?
- Which devices do you currently use to access our product?
- Which of the following features would you like to see improved or enhanced?
2. Context Screen: A context screen refers to a specific page that provides background information, instructions, or context to respondents before they begin responding to the questions in the study.
3. Thumb Up/Down: Thumbs Up/Down questions provide a binary choice for respondents to indicate their agreement or disagreement. They are useful for quickly assessing sentiment or preference.
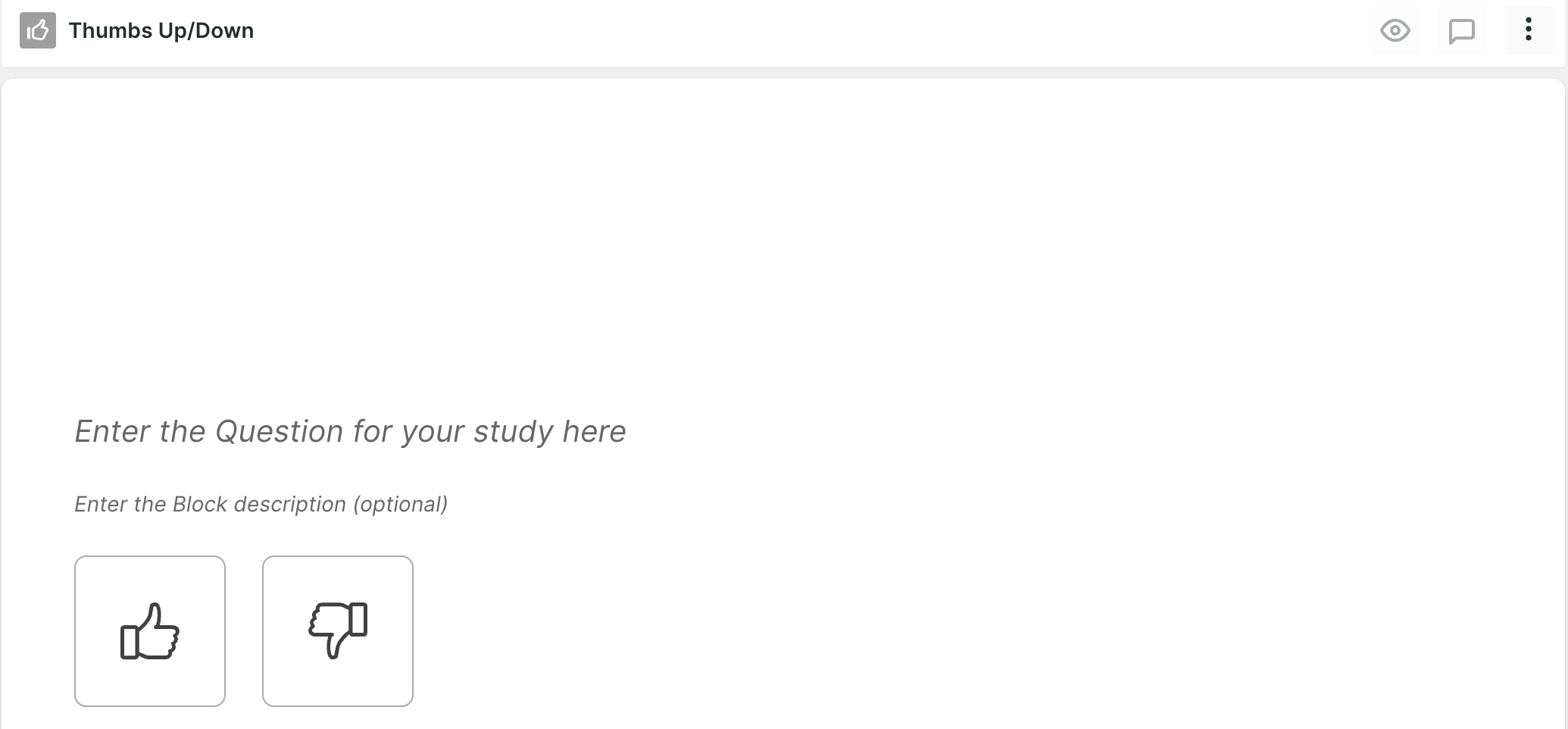
Question Example:
- Were you able to find the product details page easily and access the information you needed in the prototype?
- Did you find the search functionality helpful in finding the information you were looking for? (Thumbs Up/Thumbs Down)
- Was the onboarding process clear and informative? (Thumbs Up/Thumbs Down)
4. Likert Scale: This question type involve respondents rating a particular attribute or experience on a numerical scale. In UX research, likert scale questions are effective for measuring attitudes, satisfaction levels, or preferences.
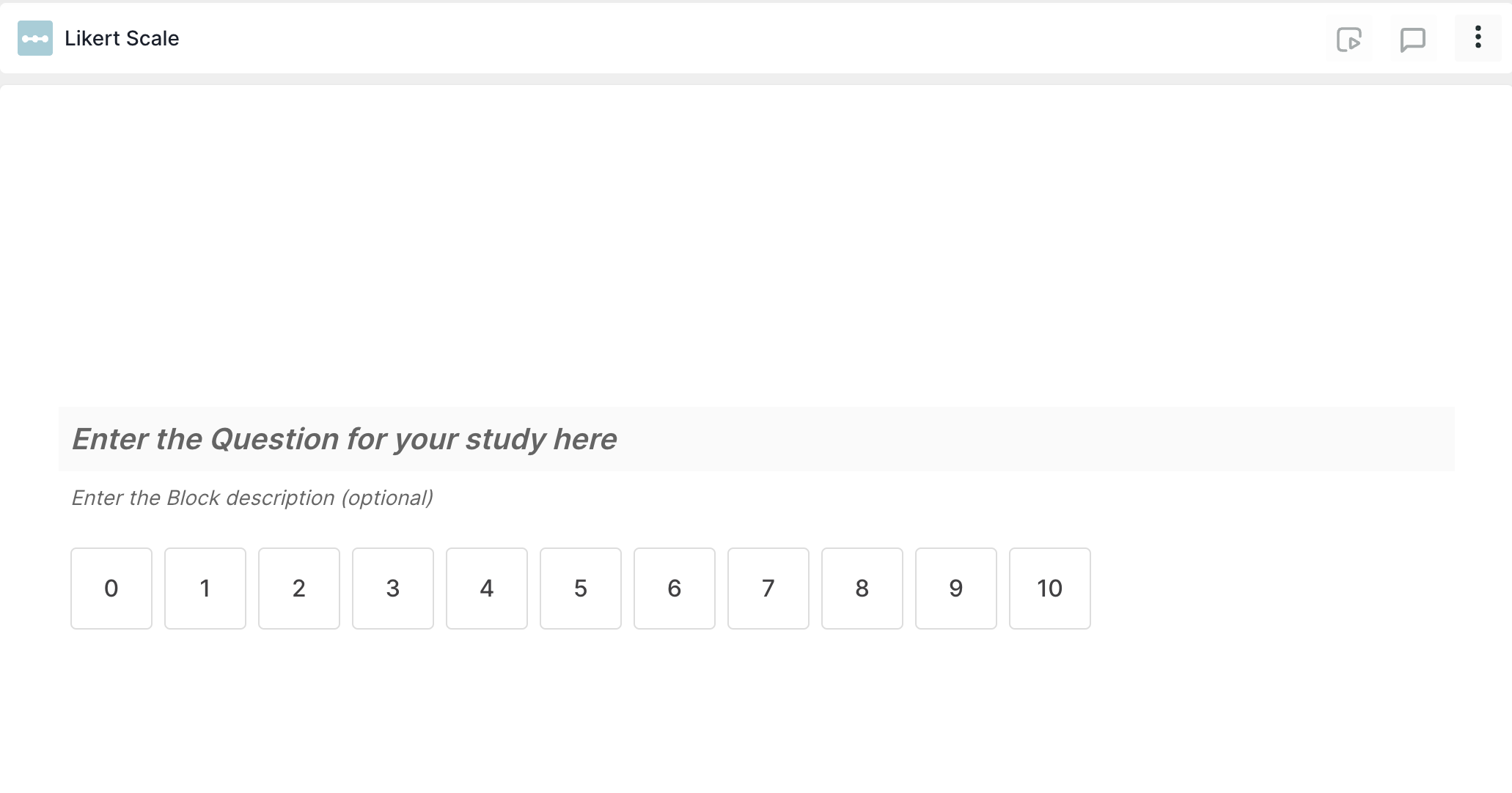
Question Example:
- On a scale of 0 to 10, how easy was it to navigate through our website?
- How likely are you to continue using our product in the future? (0 - Not likely at all, 10 - Extremely likely)
- On a scale of 0 to 10, how likely are you to recommend our app to a friend or colleague?
5. Multiple Choice Question: This question type provide respondents with a set of predefined options, and they can select a single choice. In UX research, multiple-choice questions are useful for gathering structured feedback and understanding user preferences.
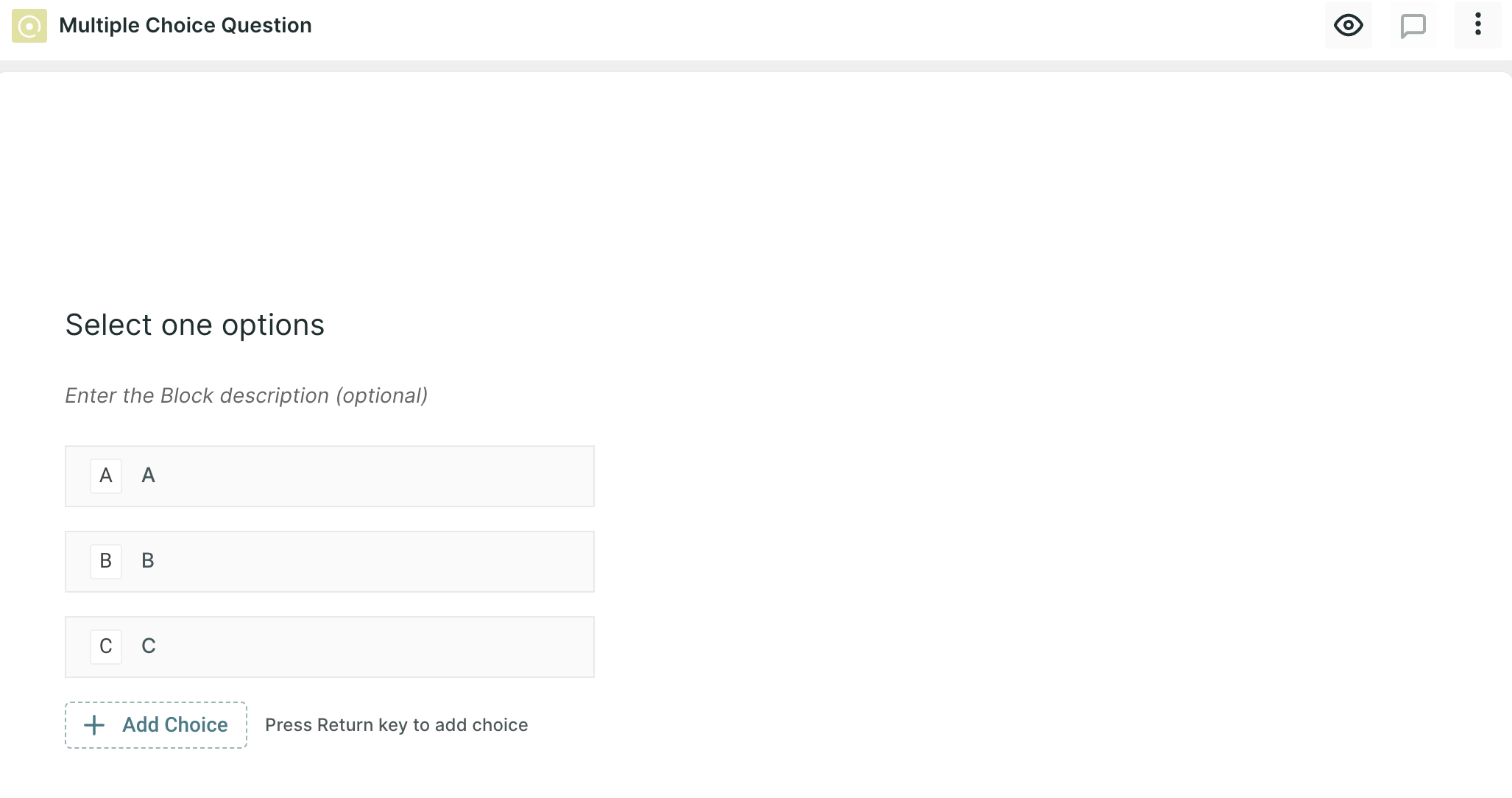
Question Example:
- Which colour scheme do you find more visually appealing for our website?
- Which version of the homepage do you find more engaging and persuasive in terms of encouraging sign-ups?
- Given the choice between two different layouts, which one do you prefer for displaying product descriptions?
- What is your primary reason for visiting our website? a) Researching products/services b) Making a purchase c) Seeking customer support d) Other (Please specify)
- Which browser do you primarily use to access our web application? a) Google Chrome b) Mozilla Firefox c) Safari d) Other (Please specify)
6. Paragraph Question: Paragraph questions prompt respondents to provide detailed and open-ended responses in their own words. This question type is used when you don't want the respondents to give answers from the limited set of options and look for details in the responses.
Question Example:
- After viewing the homepage for 5 seconds, what is your initial impression or understanding of our brand or product?
- Tell us about any challenges you faced while using our app and how we can improve.
- Please share any additional feedback or suggestions you have for improving our user interface.
- Describe a specific instance where our product exceeded your expectations.
7. Short Answer Question: This question type require respondents to provide brief responses in their own words. These questions are useful for collecting concise and focused feedback.
Question Example:
- Based on the brief glimpse of the navigation menu, can you identify where you would find information about our pricing?
- What is the main reason you chose our product over competitors?
- What is one feature you would like to see added to our website?
- How did you discover our product or service?
- What challenges or frustrations do you face when using our mobile app?
8. Smiley Rating: This question type involves respondents selecting a smiley or emoticon that represents their sentiment or satisfaction level. Smiley rating questions are a quick and visually appealing way to gauge user feedback. The smiley question is a 5-point rating scale available in the form of smiley images intended to represent a range of sentiments from negative to positive.
Question Example:
- How easy or intuitive was it to complete the registration process using the prototype?
- How satisfied are you with the speed of our app? (Select the appropriate smiley rating)
- How enjoyable was your shopping experience on our website? (Select the appropriate smiley rating)How user-friendly is our website? (Select the appropriate smiley rating)
- Rate your level of satisfaction with the clarity of our instructions and guides. (Select the appropriate smiley rating)
9. Star Rating: Star rating questions ask respondents to rate a particular attribute, feature, or overall experience using a star-based scale. Star ratings provide a familiar and intuitive way for respondents to express their opinions.
Question Example:
- How would you rate the clarity of our product descriptions? (1 - Very poor, 5 - Excellent)
- Rate the overall performance of our app. (1 - Terrible, 5 - Outstanding)
- How would you rate the effectiveness of our search feature in delivering relevant results? (1 - Ineffective, 5 - Highly effective)
- Rate the overall design aesthetics of our mobile app. (1 - Poor, 5 - Excellent)
10. Consent Block: During the test, testers can easily access and review the contents of the Consent Block, with a simple checkbox affirming that they have read and agreed to the terms and conditions. This feature enhances transparency and ensures that testers are fully informed and compliant throughout the testing process.
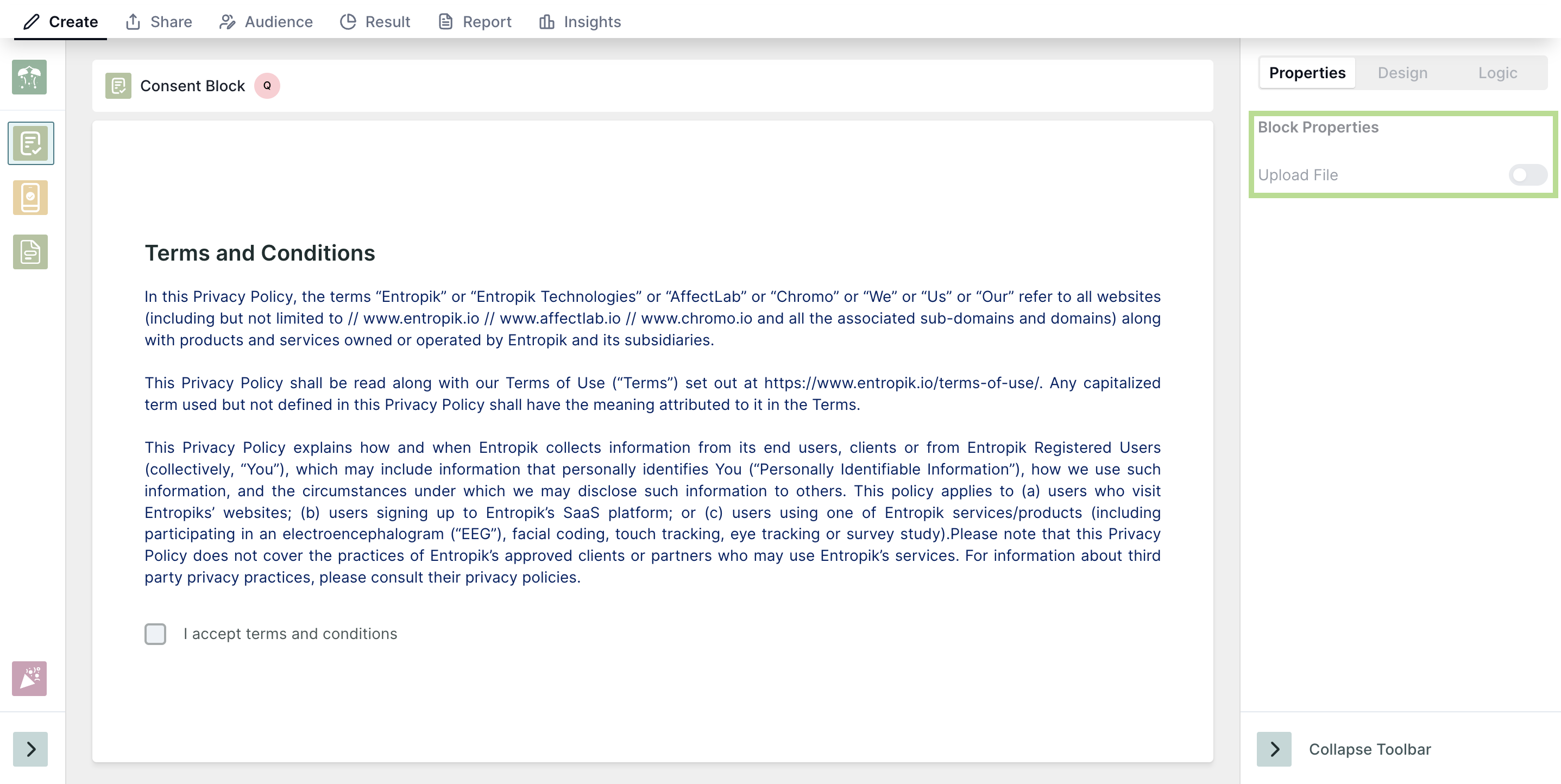
How it works?
When creating tests, users can incorporate a Consent Block, where they can add titles and descriptions, or upload files to be used as consent materials.
Unmoderated Blocks
In the Unmoderated section, you will find different types of tests for UX research studies. Here are some of the different types of tests available in the Unmoderated Block:
5-Second Testing Block: 5-Second Testing is a technique for gathering initial impressions and feedback from users. In this test, a prototype/Image/website is displayed to the respondents for 5 seconds, and their responses are gathered to understand what they noticed.

A/B Testing: In this test block, you can add two variations of your website and display each version to users to see which performs better.

Preference Test: In this test block, you can add two or more variations of your website and display each version to users to see which performs better.
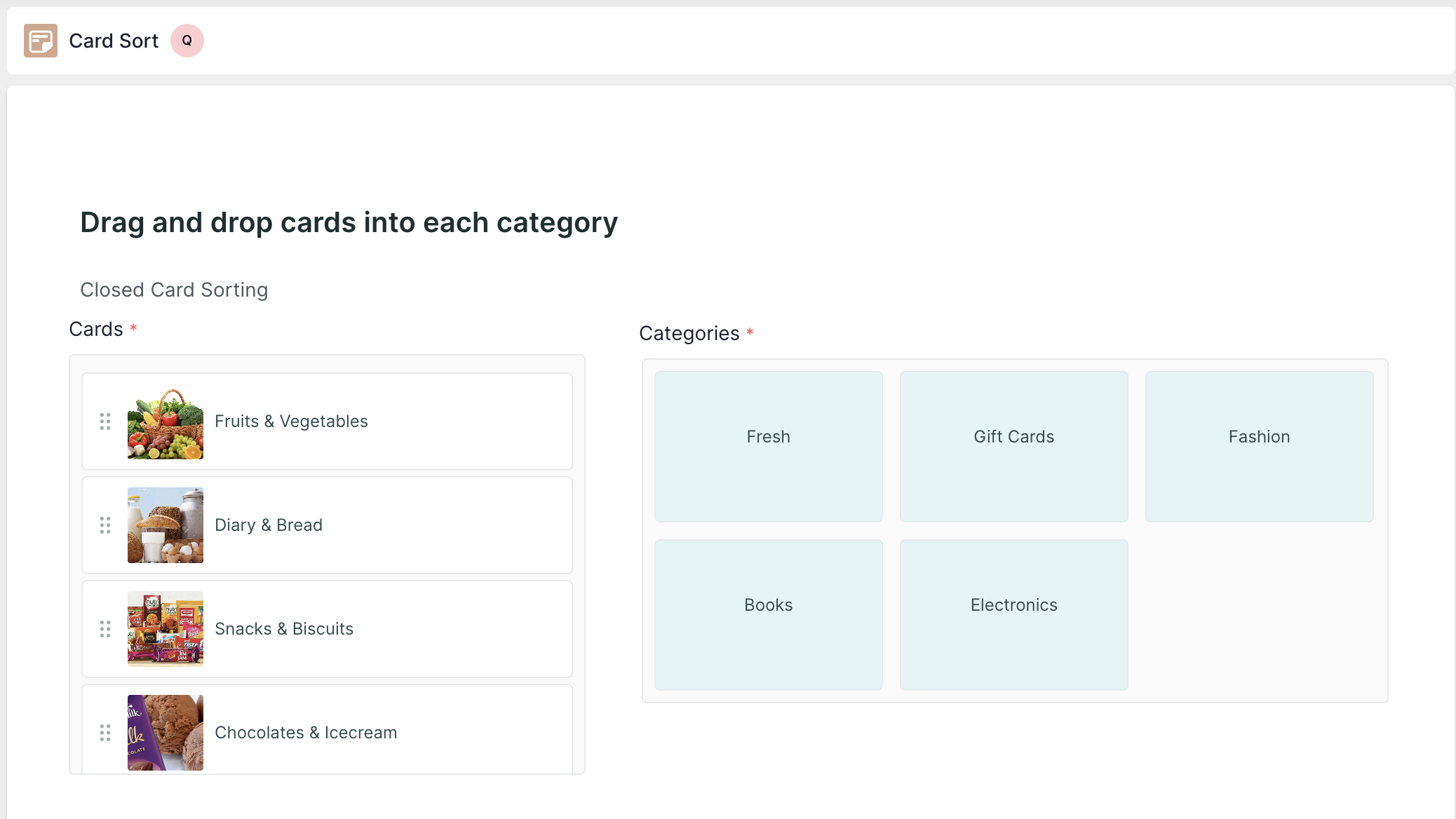
Card Sorting : In this test block, you can ask users to organize and categorize content or features, helping to understand how they expect information to be structured within the product.
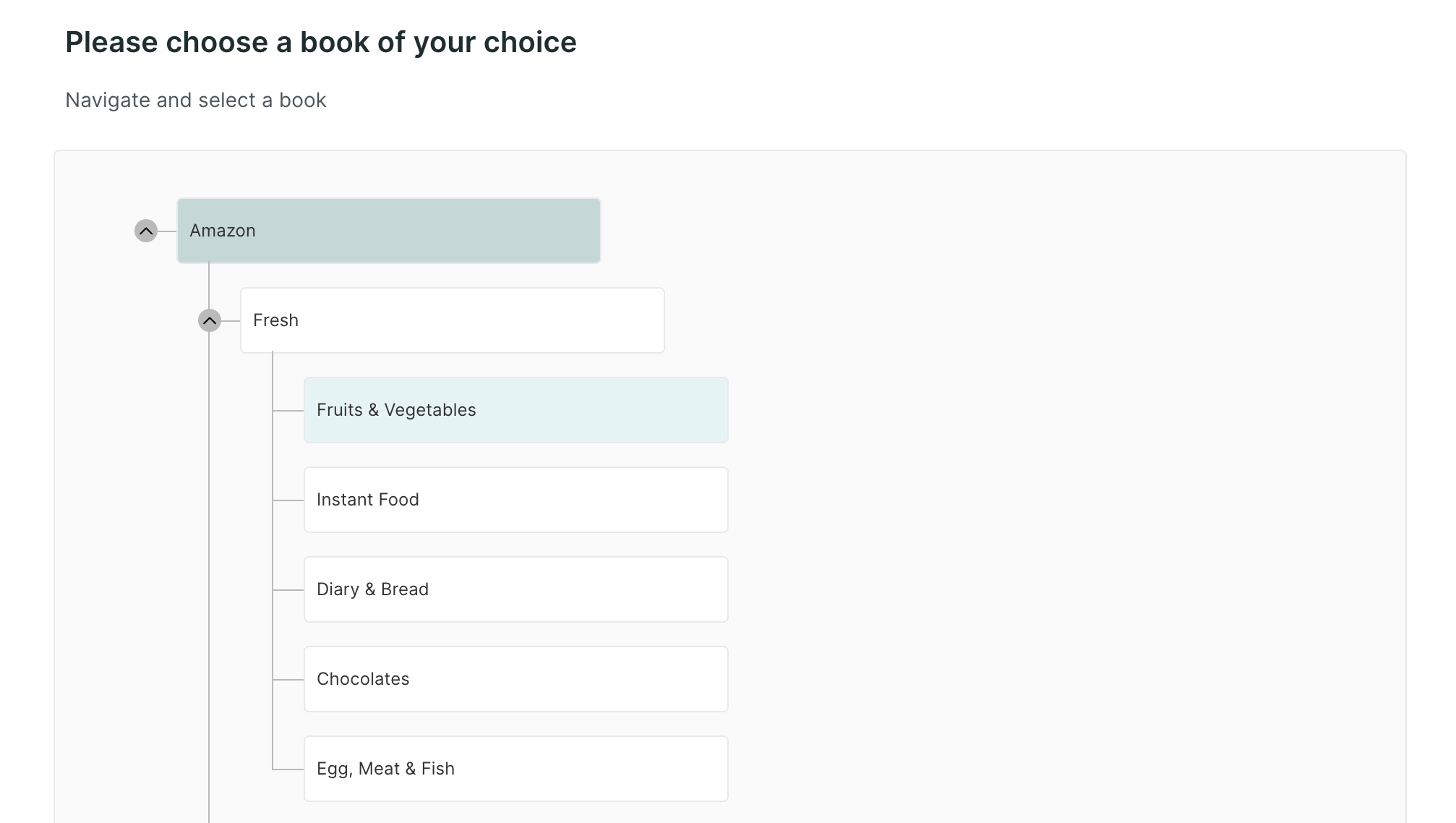
Tree Testing : This block is a usability testing method used to evaluate the effectiveness of a website or application's navigation structure. You can give tasks to users to find specific items within a hierarchical menu or sitemap, allowing designers to assess the clarity and efficiency of the navigation system.
First Click : This block focuses on users' initial interactions with a website or application interface. It records the first click made by users when attempting to complete a task, providing insights into their instinctive navigation patterns and potential usability issues.
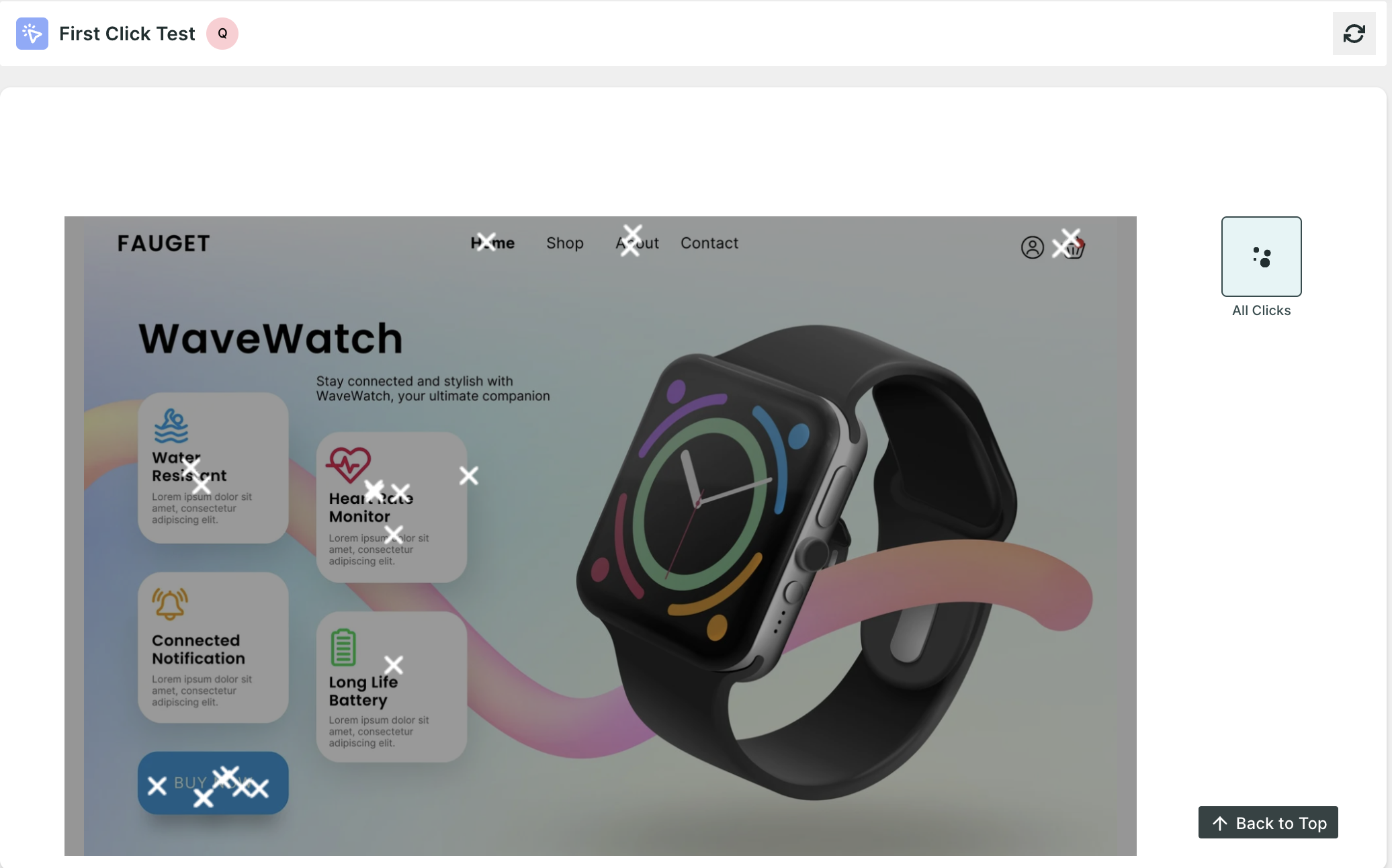
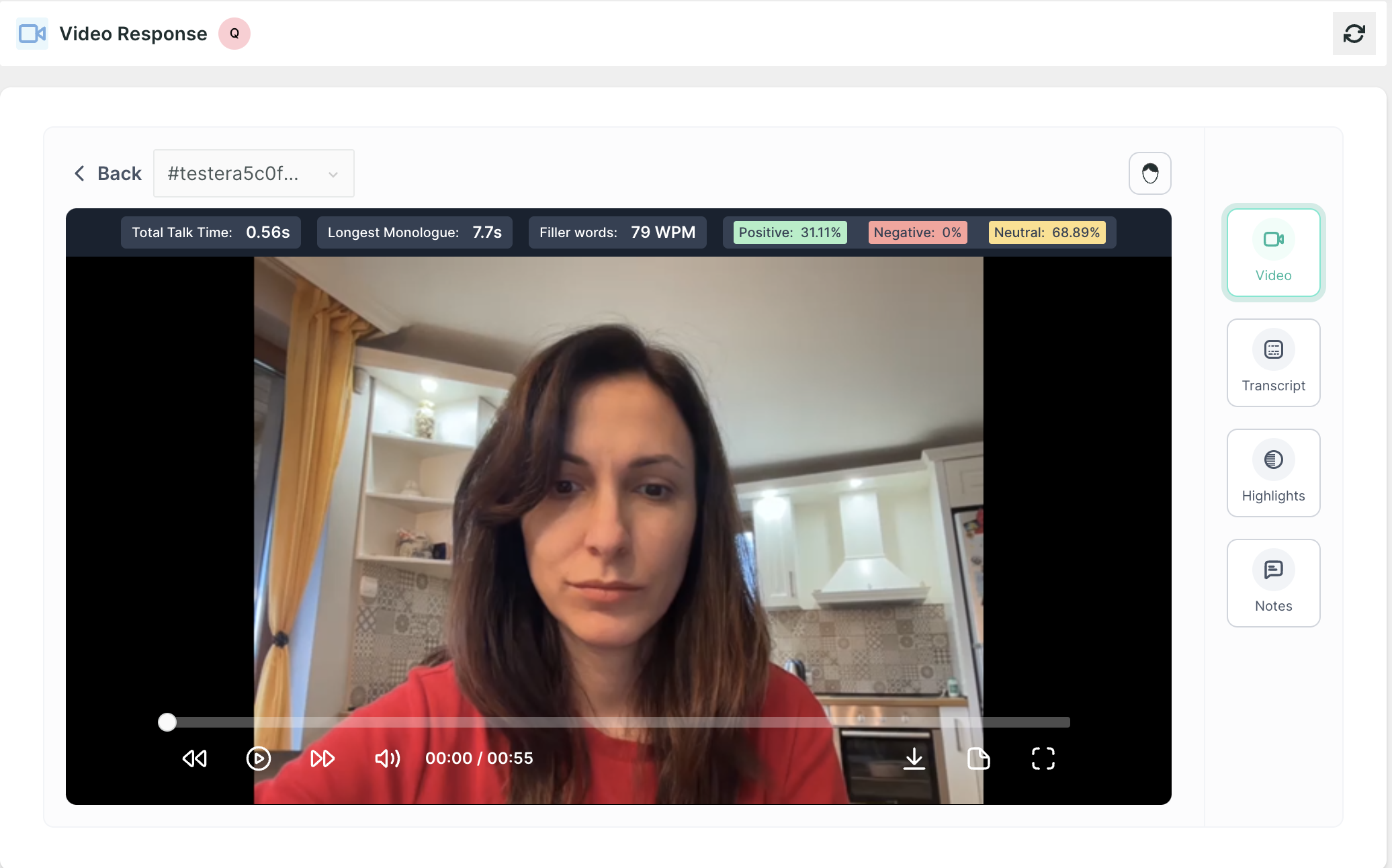
Video Response: This block allows participants to provide feedback or complete tasks by recording themselves via video, offering a rich source of qualitative data on user experiences, preferences, and interactions with the product.
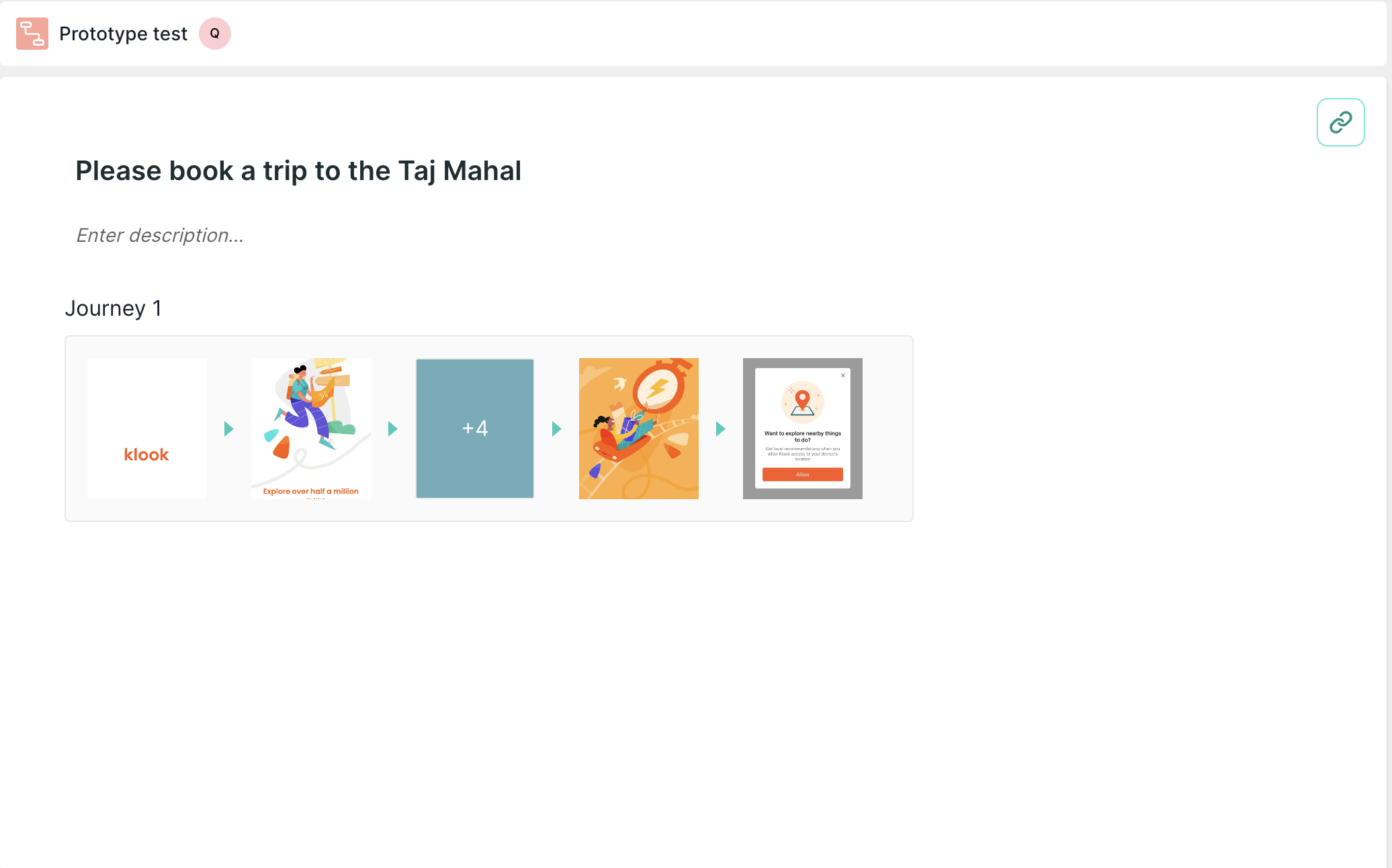
Prototype Testing: This block is a tool used in usability testing to assess the functionality and user experience of interactive mock-ups or prototypes of a product, enabling designers to gather feedback, identify areas for improvement, and iterate on design decisions before final development.
Moderated Blocks
In the Moderated section, you will find the Sessions block which you can add to your study and gather qualitative data.
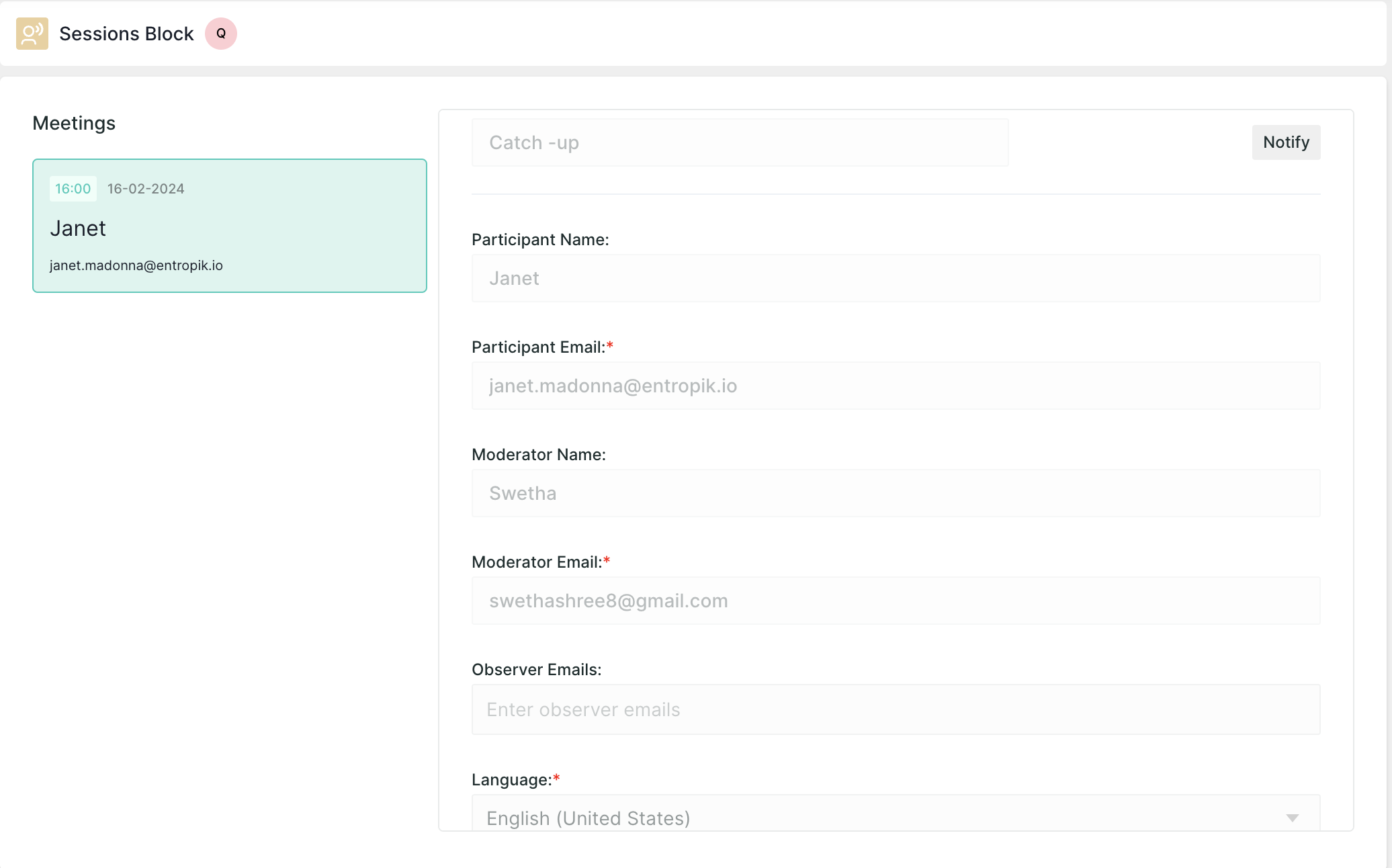
Sessions Block: This block facilitates direct interactions between a moderator and a participant in usability testing, enabling in-depth discussions, observations, and feedback gathering to uncover user insights, preferences, and pain points with a product or service.
Task Research Blocks
In this section you will find two different types of blocks which you can add to your study and get deeper insights.
1. Mobile App Testing: This block provides a structured environment for evaluating the functionality, usability, and performance of a mobile application across android devices, ensuring a seamless user experience and identifying potential issues for improvement prior to release.
How it works?
To engage in Mobile App testing with Qatalyst, users need to install the Qatalyst App from the Play Store. Once installed, they can effortlessly access and complete tests by simply copying and pasting the test link within the app.
2. Live Website Testing: This block involves evaluating the functionality, usability, and performance of a website in its real-world environment, allowing testers to assess user experience, identify issues, and optimize the site's performance while it is actively accessible to visitors.